Spatial biology is a multidisciplinary field that seeks to understand the organization and function of biological systems at different spatial scales. This field bridges the gap between traditional biology and physical sciences, allowing scientists to study biological systems from a spatial perspective, which is crucial to understanding how biological processes occur both in health and disease. Spatial biology has become increasingly important in recent years, as it has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of biological systems and offer new insights into the development of new treatments for a wide range of diseases.
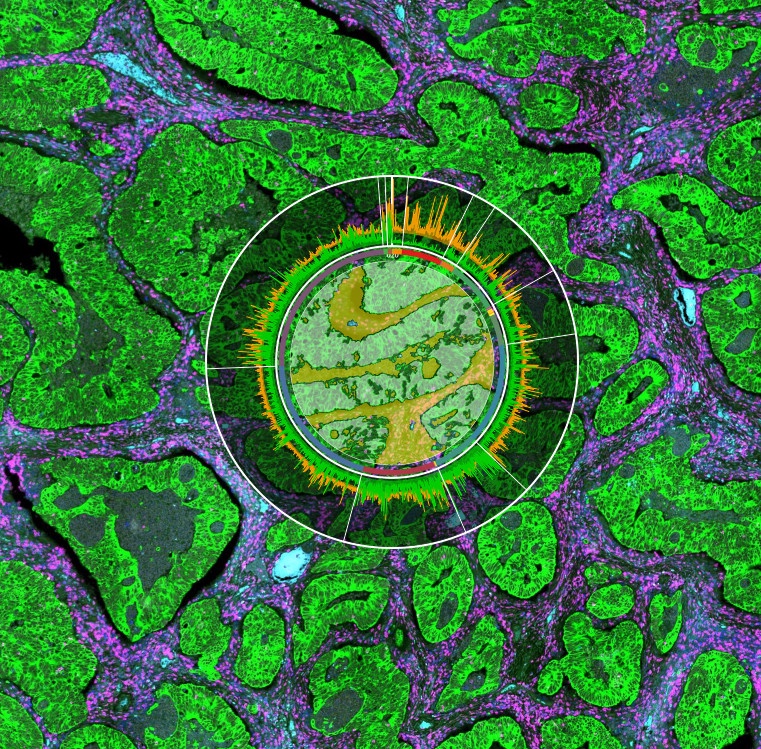
Spatial biology focuses on the spatial organization of biological systems, from the level of individual cells to entire organisms, and how this organization influences the behavior and function of these systems. The field is based on the principles of physics, chemistry, and mathematics, and uses a range of imaging technologies, such as microscopy, to visualize and analyze the spatial organization of biological systems. This approach allows researchers to gain a detailed understanding of the complex processes that occur within cells and tissues, as well as the interactions between different cells and tissues at different spatial scales.
At the cellular level, spatial biology seeks to understand how cells are organized within tissues and how this organization affects cell function. Cells are the building blocks of all living organisms, and the way they are arranged within tissues is critical to their